# Overview
Azure Application Gateway is a load balancing service that manages application traffic at the application layer (Layer 7). It provides features such as SSL termination, URL-based routing, and connectivity to web applications hosted across multiple sites.
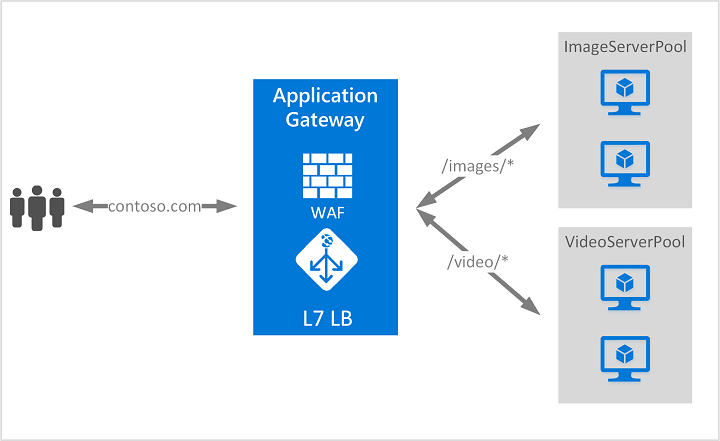
# Key Features
Azure Application Gateway offers several important features for managing and optimizing your application traffic:
- **Multi-Site Support:** Allows hosting of multiple sites on a single Application Gateway using different routing rules.
- **SSL Termination:** Simplifies your server management by offloading SSL processing to the Application Gateway.
- **Mutual Authentication:** Supports certificate-based authentication to verify client identity, enhancing security for sensitive data exchanges.
- **Wildcard Rules and Rule Priority:** Provides flexible rule configurations to handle various incoming request scenarios effectively.
# Importance
Utilizing Azure Application Gateway in an Azure Cloud Data Center is crucial for delivering efficient and secure application delivery. It enhances the performance and reliability of applications by offloading significant tasks from servers, reducing latency, and providing robust routing mechanisms. Moreover, it offers security features such as SSL termination and mutual authentication, which are vital for protecting sensitive data and maintaining compliance with industry standards.
# Use Cases
Azure Application Gateway is suitable for a wide variety of use cases within an Azure Data Center:
- **Complex Web Applications:** Manage and optimize traffic for web applications that require SSL termination and URL-based routing.
- **Multi-Site Hosting:** Deploy multiple websites on a single gateway instance by leveraging its multi-site feature and rule priority management.
- **Data Security:** Implement secure channels with SSL offloading and mutual authentication for applications that handle sensitive data.
These features and use cases make Azure Application Gateway an invaluable tool for managing web traffic in modern, cloud-based environments.