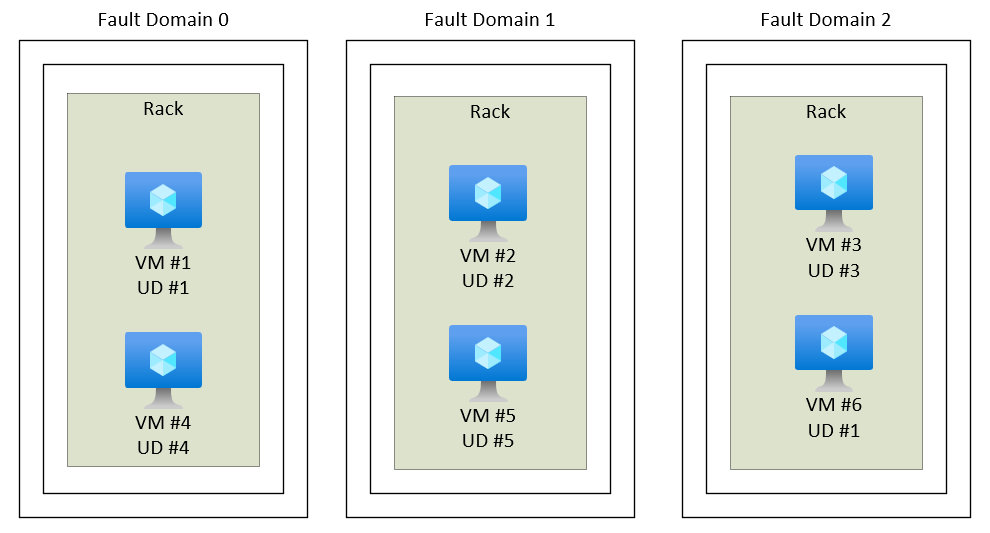
Availability sets are used to improve the reliability and availability of Azure [[Virtual Machine]] (VMs) by reducing the chance of correlated failures. VMs in an availability set are placed in different fault domains to minimize single points of failure. This setup helps achieve a 99.95% Azure service-level agreement (SLA)
The underlying Azure platform assigns an _update domain_ and a _fault domain_ to each virtual machine in your availability set. Each availability set can have up to 3 fault domains and 20 update domains. You can't change these configurations after you create the availability set.
## Update Domain
An **update domain** is a group of Azure virtual machines (VMs) and underlying hardware that can be restarted simultaneously. Each availability set can have up to 20 update domains, ensuring that not all VMs are rebooted at the same time during maintenance, thus maintaining service availability.
## Fault Domain
A **fault domain** is a group of Azure virtual machines (VMs) that share a common power source and network switch. By default, VMs are separated across up to three fault domains to minimize the risk of simultaneous failures due to hardware or power issues.
## Resources
[Availability sets overview - Azure Virtual Machines | Microsoft Learn](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/availability-set-overview)